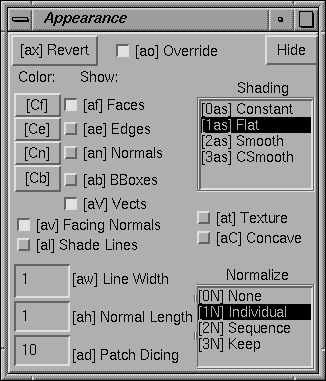
Figure 3.5: The Appearance Panel.
Next: Materials Panel, Previous: Appearance, Up: Appearance
The Appearance panel lets you change most common appearance properties of the target object.
If the target is an individual geom, then changes you make in the appearance panel apply to that geom's appearance. If the target is the World, then appearance panel changes apply to the World appearance and to all individual geom appearances. (Users have found that this is more desirable than having the changes only apply to the World appearance.) If the target is a camera, then appearance panel changes apply to the geom that was most recently the target.The five buttons near the upper right corner under the word Draw control what parts of the target geom are drawn.
The four buttons under Color labeled Faces, Edges, Normals, and BBox let you specify the color of the corresponding aspect of the target geom. Clicking on one of them brings up a color chooser panel.
This panel offers two sets of sliders: H(ue) S(aturation) V(alue), or R(ed) G(reen) B(lue), each in the range 0 through 1. The square shows the current color, which is given numerically in both HSV and RGB systems in the corresponding text boxes.In the HSV color system, hue H runs from red at 0, green at .333, blue at .667, and back to red at 1.0. Saturation gives the fraction of white mixed into the color, from 0 for pure gray to 1 for pure color. Value gives the brightness, from 0 for black to 1 for full brightness.
Pressing the RGb or HSV button at top center switches the sliders to the other color system. You can adjust colors either via the sliders, or by typing in either the RGB or HSV text boxes.
Click OK to accept the color that you have chosen, or Cancel to retain the previous color setting.
The SHADING browser lets you specify the shading model that Geomview uses to paint the target geom.
The Facing Normals button on the Appearance panel indicates whether or not Geomview should arrange that normal vectors always face the viewer. If a normal vector points away from the viewer the color of the corresponding face or vertex usually is darker than is desired. Geomview can avoid this by using the opposite normal in shading calculations. This is the default. Using Facing Normals can give strange flickering dark or light shading effects, though, near the horizon of a fairly smooth facetted object. Press this button to use the normals given with the object.
The three text fields in the lower left corner of the Appearance panel are:
The Revert button on the Appearance panel undoes all settings in the target appearance. This causes the target geom to inherit all its appearance properties from its parent.
The Appearance panel's Override button determines whether appearance controls should override settings in the objects themselves – for example, setting the face color will affect all faces of objects with multi-colored facets. Otherwise, appearance controls only provide settings which the objects themselves do not specify. By default, Override is enabled. This button applies to all objects, and to all appearance-related panels.